Computational Bridge Aerodynamics
A parametric digital process for numerical wind structure interaction analysis
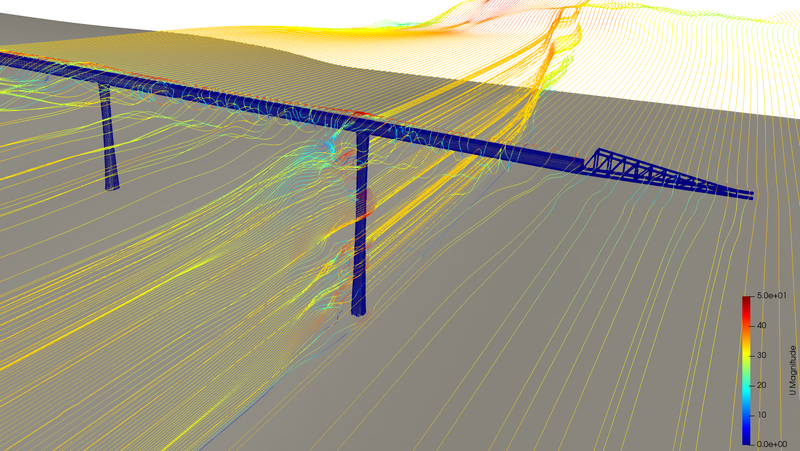
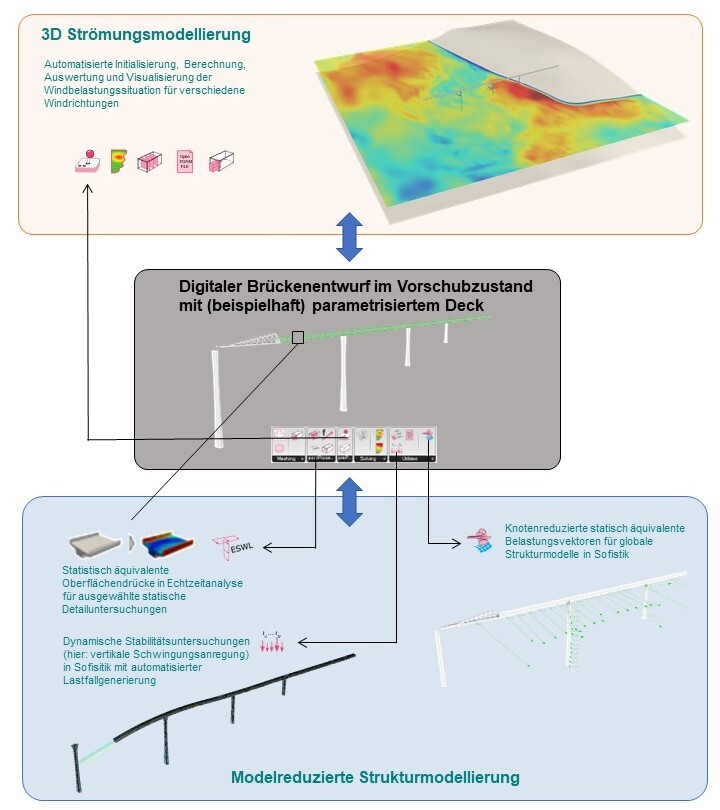
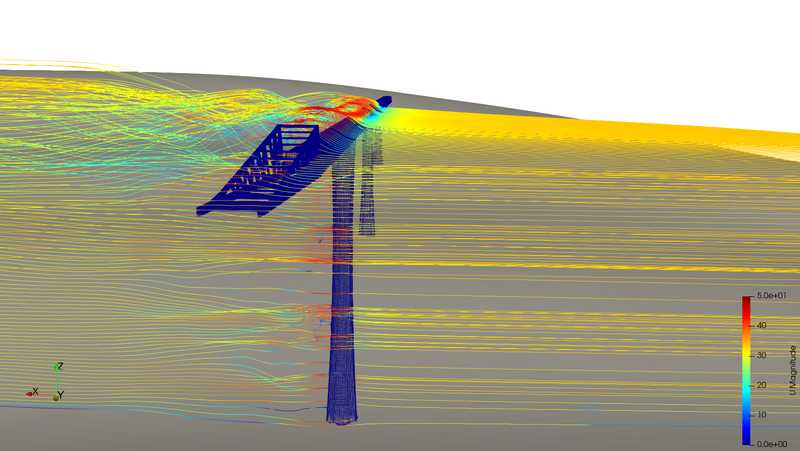
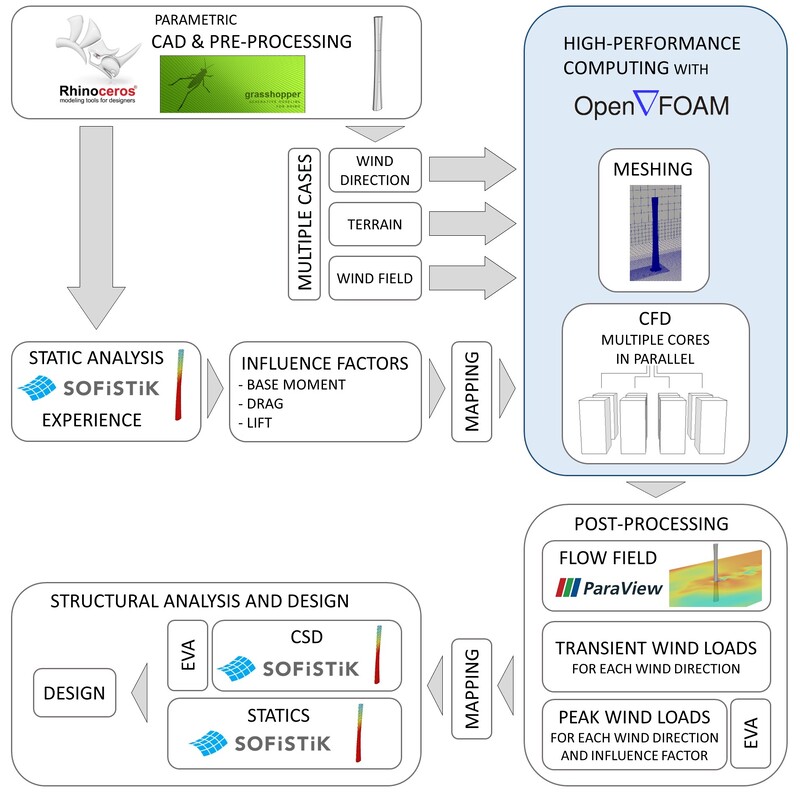
The research project explores the practical application of computational wind engineering in structural analysis. Collaborating with the Technical University Munich and Grassl Ingenieure, the study focuses on recent advancements in digital workflows that facilitate structural engineers in dealing with wind loading challenges, especially for complex structures. Historically, wind loading analysis relied on physical wind tunnels, but recent developments in supercomputing have made computational fluid dynamics (CFD) more practical. The authors' research, implemented in Rhinoceros 3d's Grasshopper plugin, details a digital workflow emphasizing pre- and post-processing on a parametric Windows system, while CFD analysis occurs on a Linux-based supercomputing cluster. The paper outlines post-processing capabilities for response and quasi-static analyses, with a focus on implementing effective static wind load distribution for generating quasi-static load cases. Current developments, illustrated with examples, are ongoing, including the integration of quasi-static load cases in the automated workflow.